4 Key Biodegradable Packaging Materials for Food and Beverages
The food and beverage industry is often challenged by the environmental repercussions of conventional packaging materials. In response to this challenge, a wave of innovation has ushered in a new era of sustainable packaging.
Biodegradable packaging emerged not merely as an alternative but as an integral component in reshaping the industry’s impact on the planet. This exploration will navigate the landscape of biodegradable packaging materials, unveiling their unique attributes and applications. Beyond their immediate benefits, these materials resonate with the overarching goals of creating a circular economy—one where packaging materials harmonize with the environment rather than burden it.
This article focuses on the applications of key biodegradable materials for packaging specifically tailored for food and beverages. From bioplastics to edible coatings, these materials signify a paradigm shift towards eco-conscious choices that address the urgent need to reduce plastic waste and lower carbon footprints.
4 Biodegradable Food and Beverage Packaging Materials
1. Compostable paper and cardboard
Compostable materials are those that can undergo biological decomposition in a compost environment, turning into nutrient-rich soil. In the context of packaging, compostable paper and cardboard provide an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials. These materials break down naturally, contributing to the circularity of the packaging life cycle.
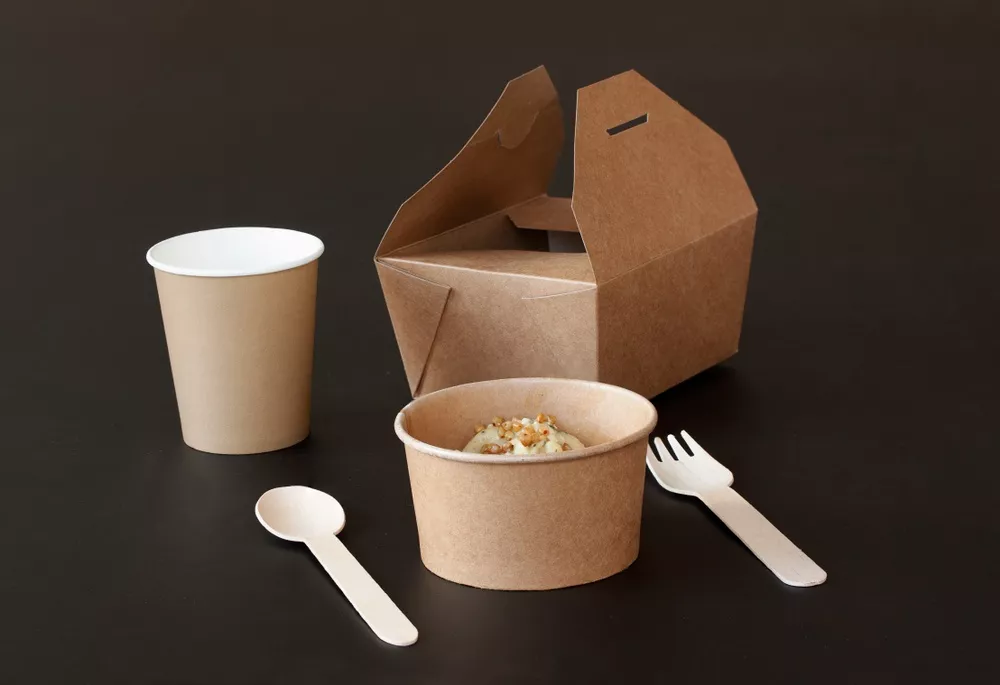

Compostable paper and cardboard find applications across a spectrum of packaging formats, showcasing their versatility and adaptability. Take, for instance, food containers made from compostable paper. These containers are not only sturdy and practical but also reduce the environmental impact associated with conventional plastic containers. Similarly, compostable cardboard trays are employed for packaging fruits, vegetables, and other perishable items, providing a sustainable solution for short shelf-life products.
Food and Beverage Packaging Designs Using Compostable Materials
The flexibility of compostable paper and cardboard allows for innovative packaging designs. Companies are moving beyond basic shapes to experiment with more intricate designs that enhance functionality and aesthetics.
- Foldable compostable boxes – these takeout boxes not only reduce waste but also offer a convenient and eco-friendly solution for consumers on the go. Alternatively, sustainable folding cartons made of compostable kraft paperboard are another economical packaging solution that can be used in hot or cold and wet or dry food service applications.
- Compostable bowls and cups – Companies like Chipotle have transitioned to compostable bowls and cups, which not only reduces their environmental footprint but also sets a precedent for other fast-food chains to follow suit. In the coffee industry, A&W Canada has also introduced compostable cups, demonstrating a commitment to reducing the environmental impact of its single-use packaging.
- Coffee cup sleeves – compostable cup sleeves have become popular in the beverage industry, providing insulation without the need for non-biodegradable alternatives.
2. Bioplastics
Bioplastics are polymers derived from biological sources, often plant-based, as opposed to conventional plastics that rely on fossil fuels. These materials can be either biobased, biodegradable, or a combination of both. Biobased plastics are made from renewable resources, while biodegradable plastics can break down into natural components under specific conditions.
The shift towards bioplastics is motivated by their numerous advantages. Firstly, these materials are renewable, reducing dependence on finite fossil fuel resources. Bioplastics also have the potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. Furthermore, their biodegradable variants contribute to mitigating plastic pollution in landfills and oceans.
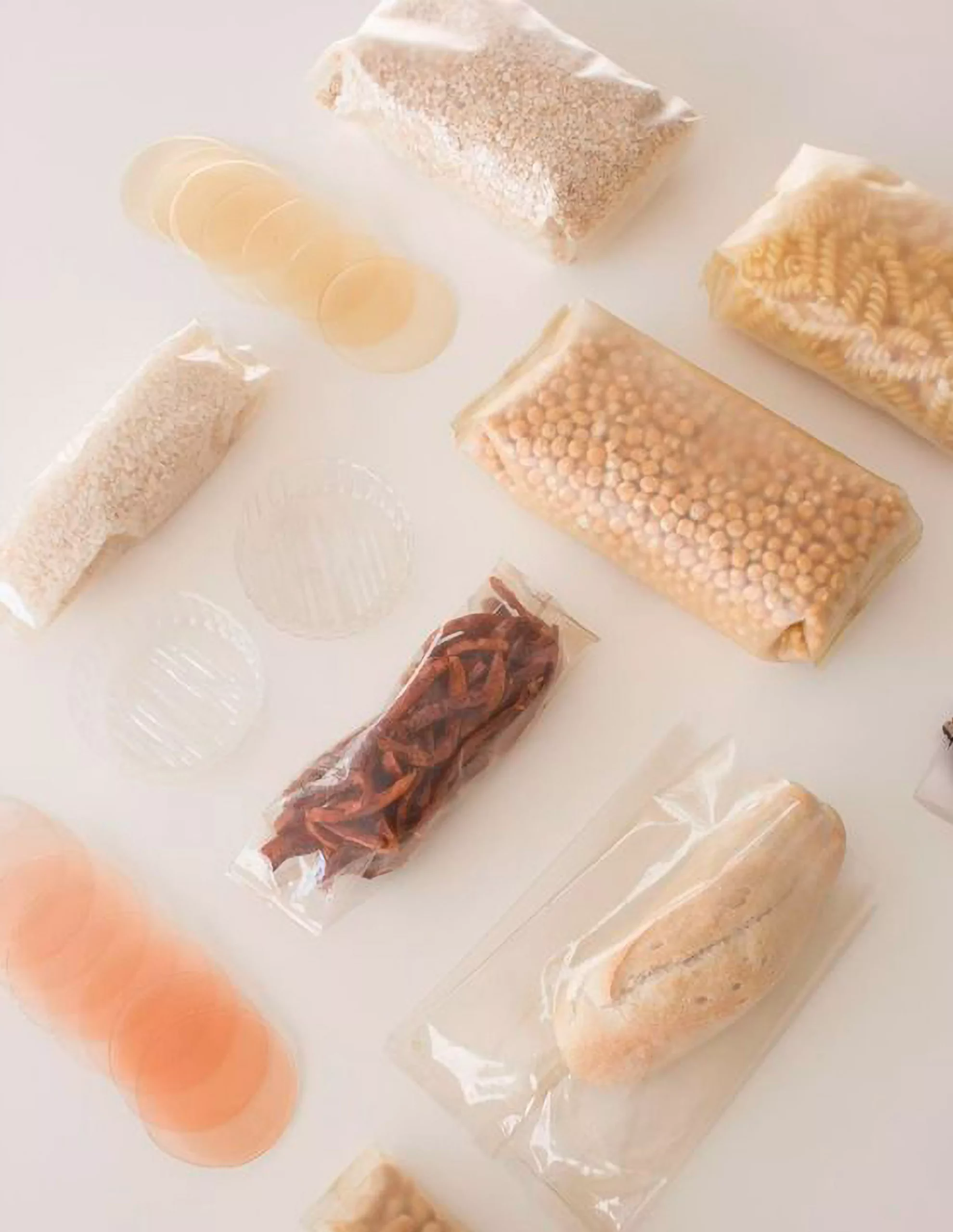

Types of Bioplastics for Food and Beverage Packaging
Several types of bioplastics are finding diverse applications in the food and beverage industry.
- Polylactic Acid (PLA) – derived from cornstarch, PLA is a transparent and versatile bioplastic, making it ideal for clear containers, biodegradable beverage packaging, and even biodegradable straws. It has gained popularity in the single-use plastic replacement market.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) – produced by microorganisms, PHA is not only biodegradable but also exhibits similar properties to traditional plastics. This makes it suitable for a range of applications, from food packaging films to disposable cutlery.
- Starch-based plastics – often a blend of starch and other biopolymers; starch-based plastics are employed in food packaging to create items like trays, clamshells, and bags. These materials offer good barrier properties and can be used for short-shelf-life products.
The successful integration of bioplastics into the packaging industry is exemplified by companies adopting these materials for their products. Coca-Cola’s PlantBottle technology incorporates sugarcane-derived polyethylene in its PET bottles. This move has significantly reduced the carbon footprint of their packaging.
Similarly, various packaging companies are paving the way for eco-friendly custom packaging solutions by offering a range of bioplastics tailored for multiple applications. These real-world examples highlight not only the technical feasibility but also the economic viability of incorporating bioplastics into mainstream packaging practices.
3. Biodegradable films
Biodegradable films are thin sheets of material designed to protect and preserve food and beverages while being capable of breaking down into natural components. One example of a biodegradable film material is cellophane, derived from plant cellulose. Cellophane films are transparent, versatile, and can be used for various packaging applications.
Biodegradable films stand out in comparison to traditional plastic films due to their environmentally friendly nature. Take, for instance, the traditional plastic overwrap for magazines or multipacks of beverages. Replacing this with a biodegradable film not only reduces plastic waste but also contributes to a more sustainable end-of-life scenario.
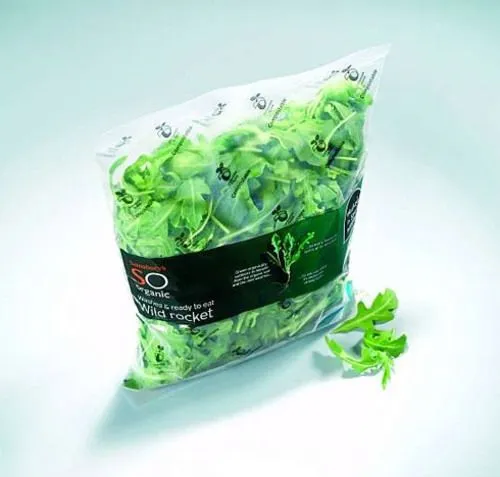

Applications of Biodegradable Films in Food and Beverage Packaging
The applications of biodegradable films in the food and beverage industry are diverse and growing. Some notable examples are:
- Shrink wrap for fresh produce – this type of film provides a breathable yet protective covering for fruits and vegetables, extending their shelf life while ensuring minimal environmental impact.
- Snack packaging and individually wrapped products – single-serve food items have embraced biodegradable films. These films cater to the on-the-go lifestyle while addressing the ecological concerns associated with single-use packaging.
- Edible biodegradable films – often made from materials like seaweed or fruit extracts. They not only serve as biodegradable food packaging but can also be consumed along with the food product. This innovation not only eliminates packaging waste entirely but also offers a unique and sustainable consumer experience.

4. Edible coatings
Edible coatings are thin layers of edible material applied to the surface of food items to extend shelf life, improve freshness, and reduce waste. These coatings are typically made from natural ingredients such as wax, starch, proteins, or even fruit extracts. Unlike traditional packaging, edible coatings eliminate the need for separate disposal and contribute to a more circular approach to packaging.
Regulatory bodies play a significant role in ensuring that these coatings meet the necessary safety standards for consumption. Ingredients used in edible coatings are often carefully selected to comply with food safety regulations, making them a viable and safe option for direct contact with food.
Additionally, the concept of edible coatings aligns with the broader movement toward cleaner labels and transparency in food production. Consumers are increasingly interested in knowing not just what goes into their food but also what goes around it as packaging.
Applications of Edible Coatings in the Food and Beverage Industry
Edible coatings offer creative applications in the industry. In particular, edible wax coatings protect fruit and vegetable produce from external factors and create a thin, natural barrier that can be consumed along with the skin, eliminating the need for plastic packaging.
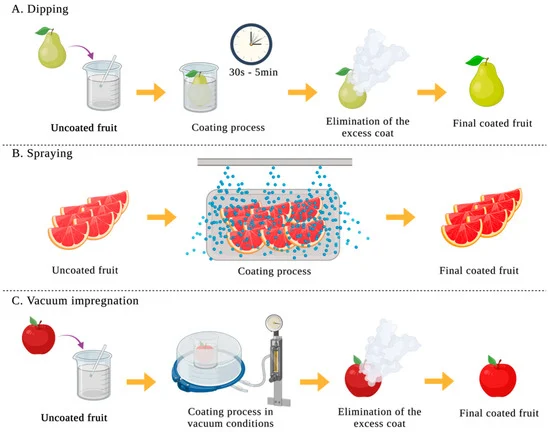
The future of edible coatings holds exciting possibilities for further innovation. Researchers are exploring advanced formulations to enhance the functionality of these coatings, such as incorporating antimicrobial properties to prolong shelf life even further. As technology and understanding of food science progress, edible coatings may become a staple in the packaging landscape.
Embracing Sustainability in Every Package
Biodegradable materials mark a shift towards a more sustainable and responsible future and unveil a diverse toolkit for industry leaders to adopt. These materials not only offer eco-friendly alternatives but also pave the way for a circular economy where packaging materials align with the principles of environmental harmony.
The positive impact of embracing biodegradable packaging materials extends beyond mitigating plastic pollution; it encompasses a reduction in carbon footprints, increased consumer trust, and a fundamental shift in the industry’s ethos. As brands and consumers alike recognize the urgency of adopting sustainable practices, the adoption of eco-friendly materials becomes a strategic imperative.
To propel this momentum further and explore how your business can adopt sustainable packaging solutions, partner with an experienced sustainable packaging manufacturer. Reach out to Meyers experts and foster innovation and responsibility in every package you create.

