All About Printing Inks: Innovations, Types, and Trends
Printing inks are essential tools for different industries across the board. From the food and beverage to the packaging and labeling industries, printing inks enabled more efficient and effective label production for many businesses.
In 2021, the printing ink market’s value was $18 billion. Experts expect this number to reach $25.62 billion by 2029. The forecasted growth is due to the increasing demand for printing inks in metal cans, tags and product labels, and flexible materials.
Whether a small retail owner or an industry expert, everyone in the industry should learn about printing inks that produce different types of packaging and achieve every business need. The guide below will provide the necessary information and valuable insights regarding printing inks, the other printing ink types, and their market.
What Are Printing Inks?
Printing inks are complex mixtures of chemical compounds that stain a surface to obtain an image, text, or pattern. People use them on surfaces such as paper, plastic, glass, textiles, and other product packaging types.
These compounds can be solid, liquid, or gas substances in their base form that transform state through physical, chemical, or a mixture of both drying methods.
Printing inks come in liquid or paste forms, and based on their apparent viscosity, their three main attributes are color, gloss, and transparency. Depending on the printing process and the target substrate, printing companies achieve these factors by the ink mixture’s varying proportions of vehicle, coloring ingredients, and additive components.
Coloring ingredients may come in pigments, agents, and lacquers, which manufacturers transfer by the vegetable or solvent-based vehicle from the ink fountain to the typeform. The additives stabilize the mixture and offer other desirable features, such as longevity and rub resistance.
Manufacturers utilize different drying processes, temperature applications, and chemicals to develop printing inks with unique qualities. Some of them include the following:
- High-gloss inks
- Quick-setting inks
- Heat-set inks
- Cold-set inks
- Moisture-set inks
- Metallic inks
- Magnetic inks
- Fluorescent inks
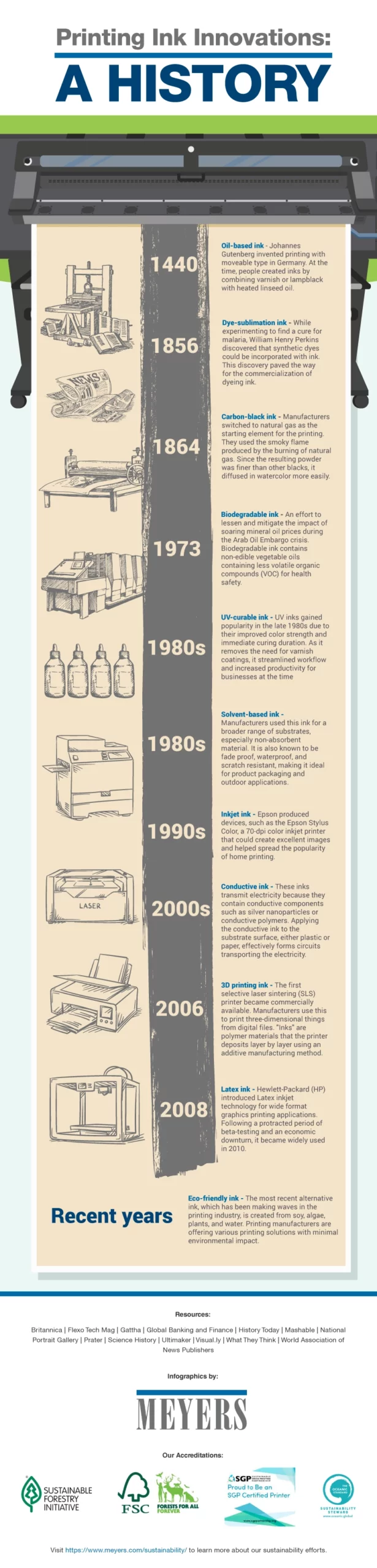
Printing Ink Innovations: A History
Digital printing and the printing ink industry have seen significant innovations to accommodate many businesses’ and consumers’ evolving needs and demands. The following provides a brief overview of ink innovations throughout history:
Common Types of Printer Inks
Modern technology has continued to develop more printing inks that ensure quality, sustainable, and cost-effective product and label manufacturing options. Here are some of them:
1. Pigment ink
This ink type consists of dry and encapsulated particles suspended in ink that offer faster drying time and longer print life. Moreover, it has better resistance to scratches, water, and UV rays, which is ideal for various product packaging.
Some may struggle with pigment ink’s color and saturation consistency as users may encounter ‘metamerism’ wherein color appearance changes based on light.
Although they last longer, pigment inks are costly and are not the best solution for detailed print work. It is best used for slicker surfaces such as stickers and transparencies because it adheres to surfaces rather than absorbs.
2. Dye-based ink
Dye-based inks are excellent mediums that offer vibrance, brightness, and overall density for high-quality printing jobs. It is made of coloration dissolved in liquid, typically water or glycol, making the dye flow better from the printer to the page. Dye-based ink also covers a broader range of colors and shades accessible worldwide.
This type of ink is ideal for commercial use as it ensures high-quality prints at a more affordable cost. However, one drawback of using dye-based inks is it tends to fade faster over time. Dye-based inks get absorbed by the paper; hence, it is more likely to break down, lose color, and blur when the printer constantly exposes the paper to sunlight or water.
3. Solid ink
Also referred to as hot melt ink, solid ink is a waxy, resin-based polymer that manufacturers melt into liquid by heated printheads. Instead of fluid ink or toner powder, solid ink is in the form of sticks, crayons, pearls, or granular materials. It produces a high-quality and precise print that is glossy and almost opaque, even with low stock.
Solid inks have some disadvantages. For one, manufacturers must regularly maintain this ink and filter out the contaminants. This practice prevents ink from clogging the print heads, which is costly. Moreover, if the printer does not have enough time to warm up, it may take more time to print the first few pages.
4. Sublimation ink
Sublimation inks consist of dye particles ground into powder and suspended in a liquid carrier, either water or solvent. Unlike other traditional ink, this type prints the reverse image onto transfer paper before placement on the desired medium. As the image is heated, the printing process causes the dye within the liquid to heat up and vaporize into a gaseous form.
During printing, one color is printed at a time, providing vibrant and distinct colors. In most cases, manufacturers use this for printing images and texts on clothing, specifically light-colored materials made with more than 50% polyester. If not used for garment printing, surfaces such as wood, ceramic, or metal require an initial polyester coating for better adherence.
5. Ribbon ink
Ribbon ink is typically used with dot matrix and thermal transfer printers to deposit the dried ink onto product packaging. When using dot matrix or impact printers, the ink-soaked ribbon is pressed against the page to print. Meanwhile, thermal transfer printers utilize heat to melt the wax or resin coating and expose the ink for printing.
Printing Inks Market Trends
1. The printing ink market’s primary application scope shifted to the packaging industry.
Initially, printing inks catered to the commercial printing and publication of newspapers, journals, and books. However, due to the digitized needs of consumers, its main application shifted to providing attractive printing solutions for promoting and marketing products with packaging materials.
2. The printing ink market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 2.5%.
The printing ink industry is on its way to a steady recovery from the pandemic. It is projected to reach a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 2.5% from 2023 to 2027. This growth is attributed to the rapid demand for food and beverage packaging printing inks.
3. There is an expected high demand for 3D printing inks.
From 2023 to 2032, experts expect 3D printing ink to lead the revenue and growth of the printing ink industry. Researchers, industrial producers, and consumer households are increasingly becoming interested in 3D printing with the recent advancements to make 3D machines more compact, accessible, and affordable.
4. In 2021, the average printing export price rose to 4.6% from the previous year.
The average printing ink export price in 2021 grew to $11,337 per tonne. Costs vary between countries, with Japan having the highest export price and the lowest average in Canada. However, most countries show modest yet steady growth in prices.
5. Non-toxic materials are being developed to manufacture printing ink.
Although rigid regulatory policies and bodies limit the usage, manufacture, and distribution of various inorganic solvents and toxic metals needed for printing ink, research initiatives are developing new economical and non-toxic materials such as graphene and modified celluloid.
Make the Most Out of Ink
The world’s ink usage has undergone various changes, each stage better than the former. Although the printing ink industry faced challenges that may have slowed its growth, it is safe to say that the varied efforts to further its development are a step closer to innovation.
As these changes continue, so do the impacts of its production on the environment. Thankfully, printing manufacturers today are making more conscious efforts to try and provide sustainable printing solutions.
Meyers Printing offers expert packaging solutions with sustainability at the forefront of its efforts. To learn more about what your business needs, contact our team of experts today.

